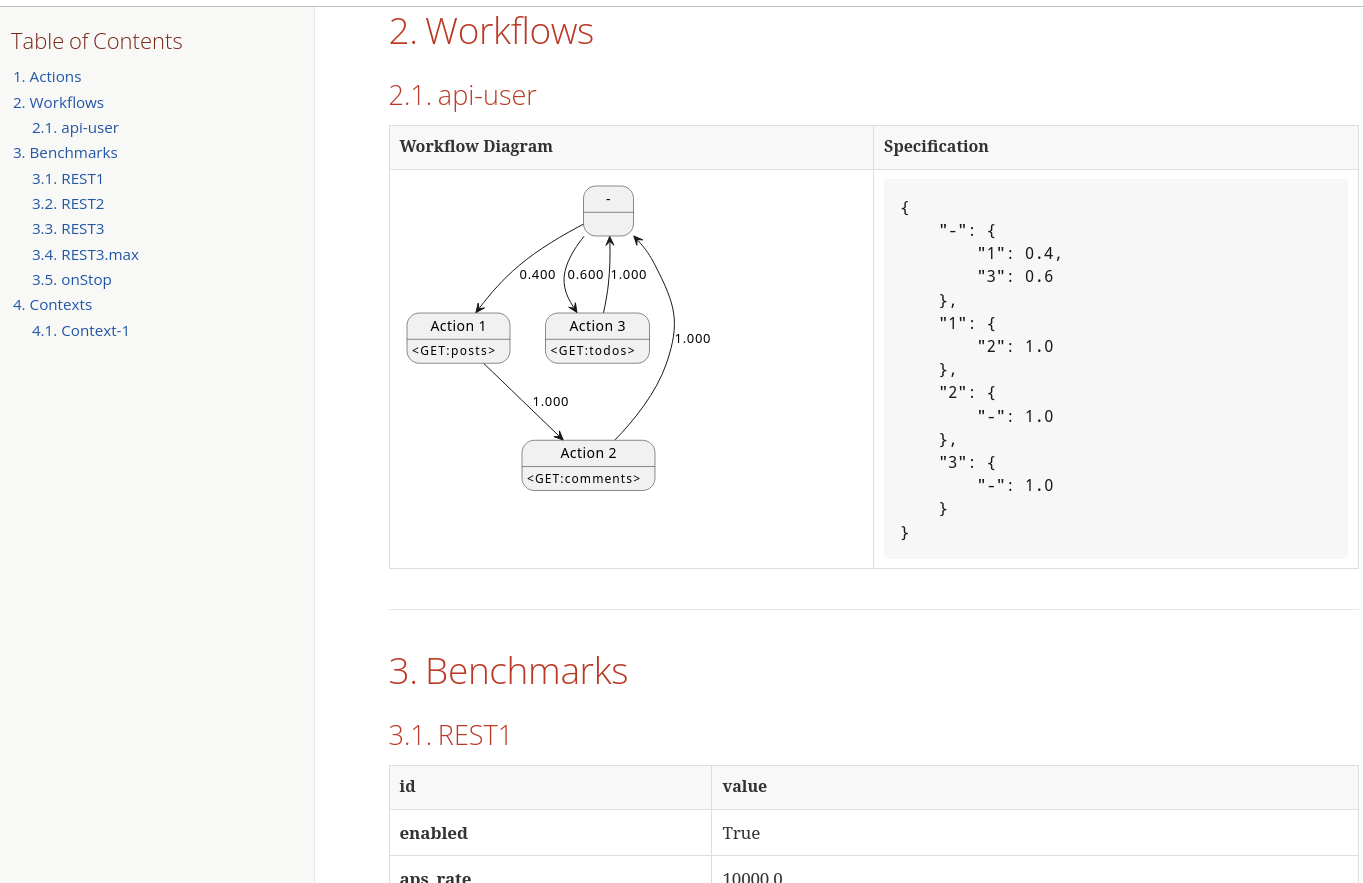
HTTP Benchmark Example
Step 1—new benchmark
Run the following command to create the Java version of the example benchmark program:
-
jbang tulip-cli@wfouche init Java
This command creates various files and directories:
├── benchmark_config.json ├── io │ └── tulip │ ├── App.java │ └── HttpUser.java ├── run_bench.cmd └── run_bench.sh |
Step 2—run benchmark
Run script run_bench.sh (Linux or macOS), or run_bench.cmd (Windows) to start the benchmark program.
While the benchmark program is running the benchmark_output.json file is incrementally updated with benchmark results.
Step 3—view benchmark results
├── benchmark_config.adoc ├── benchmark_config.html ├── benchmark_config.json ├── benchmark_output.json ├── benchmark_report.html |
── benchmark_report.json ├── io │ └── tulip │ ├── App.java │ └── HttpUser.java ├── run_bench.cmd └── run_bench.sh |
Once the benchmark is finished, a benchmark report is automatically generated from the benchmark_output.json file.
The benchmark report file is called benchmark_report.html. The benchmark script displays the benchmark report on the console using the lynx text web browser utility (as shown below).
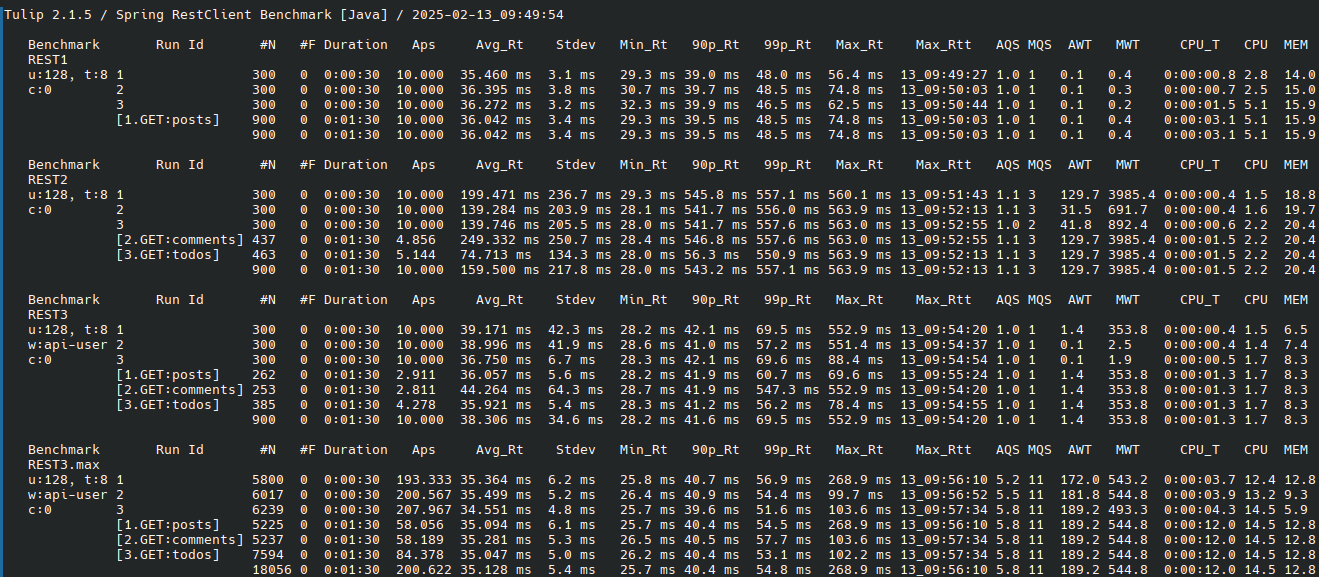
|
Open the benchmark_report.html file in a browser to view the benchmark results.
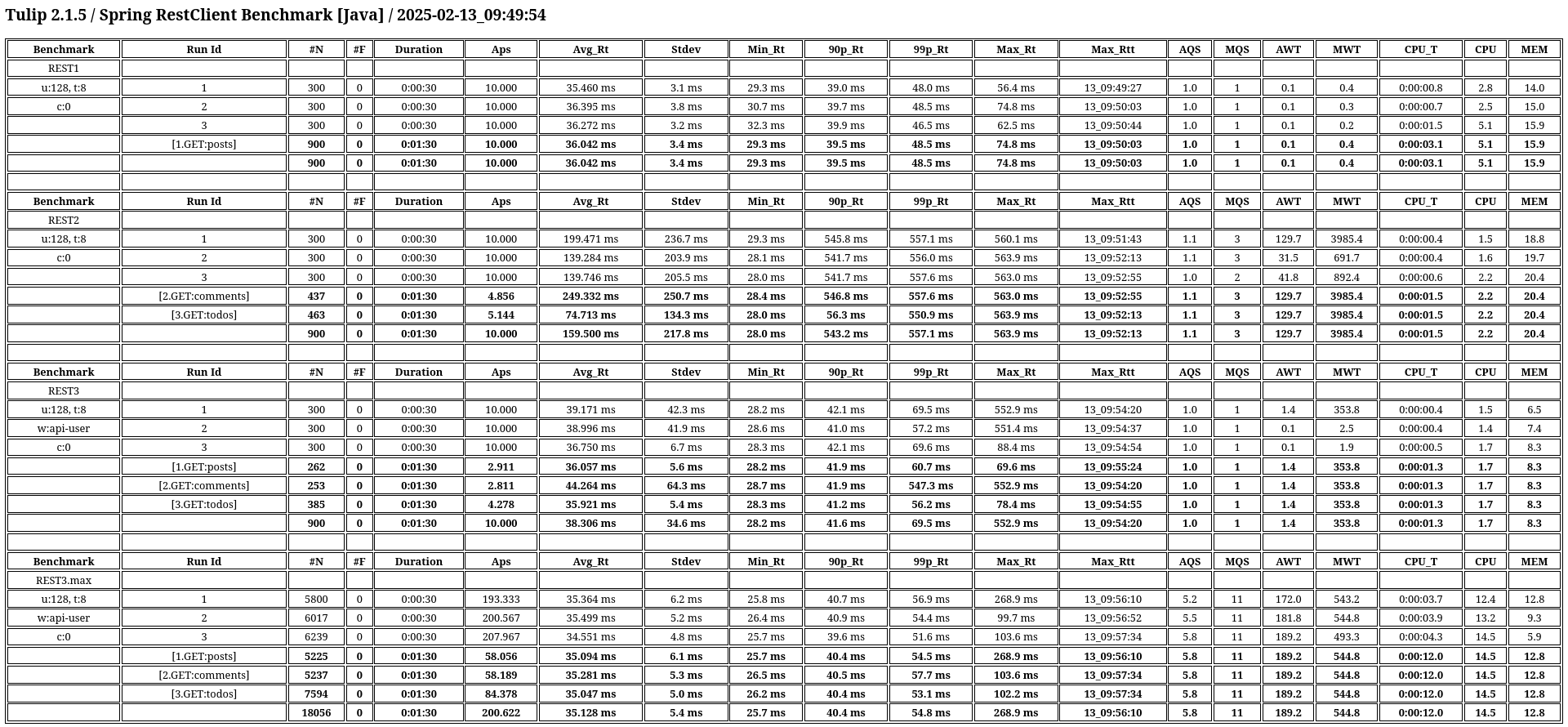
|
Step 5—view JSON summary
File benchmark_report.json contains the same results that are displayed in the HTML benchmark report. Having the results in a JSON file format, makes it easy to validate the final results.
import json
from collections import OrderedDict
filename = "benchmark_report.json"
fileObj = open(filename)
jb = json.load(fileObj, object_pairs_hook=OrderedDict)
def report(name):
print name
print " ", jb["benchmarks"][name]["actions"]["summary"]["aps"], "aps"
print " ", jb["benchmarks"][name]["actions"]["summary"]["aps_target_rate"], "aps_target_rate"
report("REST1")
report("REST2")
report("REST3")
report("REST3.max")$ jbang run jython-cli@jython json_report.py
REST1
10.0 aps
10.0 aps_target_rate
REST2
10.0 aps
10.0 aps_target_rate
REST3
10.0 aps
10.0 aps_target_rate
REST3.max
117.977777778 aps
0.0 aps_target_rate